What Is the Navajo Medicine Wheel?
The Navajo Medicine Wheel, also known as the Navajo Sacred Circle, is a profound and multifaceted symbol central to the Navajo (Diné) worldview and spiritual practices. It represents a holistic understanding of the universe, the interconnectedness of all things, and the path to balance and well-being. Unlike some other medicine wheels found among various Native American tribes, the Navajo Medicine Wheel is not a physical structure or monument, but rather a concept and a framework for understanding the world.
Origins and History
The origins of the Navajo Medicine Wheel are deeply rooted in the Navajo creation stories and cultural traditions. The Navajo people, known as the Diné (meaning "the People"), have inhabited the Southwestern United States for centuries. Their traditional beliefs and practices have evolved over time, integrating elements from their ancestors and interactions with other tribes. The Medicine Wheel is a fundamental aspect of this rich cultural heritage, passed down through generations of healers, medicine men, and spiritual leaders.
The Circle’s Symbolism
<img src="https://www.potawatomi.org/wp-content/uploads/Medicine20Wheel.jpg" alt="
What Is the Navajo Medicine Wheel?
” title=”
What Is the Navajo Medicine Wheel?
“>
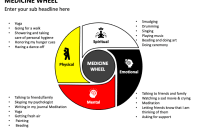
At its core, the Navajo Medicine Wheel is a circle, symbolizing the cyclical nature of life, death, and rebirth. It encompasses all aspects of existence, from the physical to the spiritual. The circle is divided into four quadrants, each representing specific elements, directions, seasons, and aspects of the human experience.
-
Directions: The four directions – East, South, West, and North – are fundamental to the Medicine Wheel. Each direction is associated with specific colors, elements, and symbolic meanings:
- East: The East is associated with the color white, the element of air, the beginning of the day, and new beginnings. It represents enlightenment, wisdom, and the spiritual realm.
- South: The South is linked to the color blue, the element of water, and the summer season. It symbolizes growth, youth, and emotional development.
- West: The West is connected to the color black, the element of earth, and the fall season. It represents introspection, self-awareness, and the journey into the darkness.
- North: The North is associated with the color yellow, the element of fire, and the winter season. It symbolizes wisdom gained through experience, old age, and the culmination of life’s journey.
-
Elements: Each direction is linked to an element of nature: air, water, earth, and fire. These elements represent the building blocks of the physical world and the interconnectedness of all things. They also relate to the different aspects of the human experience:
- Air: Represents the mind, thoughts, and the breath of life.
- Water: Represents emotions, feelings, and the flow of life.
- Earth: Represents the physical body, grounding, and stability.
- Fire: Represents spirit, energy, and transformation.
-
Seasons: The four directions correspond to the four seasons of the year, reflecting the cyclical nature of life and the passage of time. Each season brings its unique energy and lessons.
-
Aspects of the Human Experience: The Medicine Wheel is also a framework for understanding different aspects of the human experience. It can be used to explore physical, emotional, mental, and spiritual dimensions of life.
The Purpose of the Medicine Wheel
The Navajo Medicine Wheel serves multiple purposes in Navajo culture and spirituality:
- Understanding the Universe: The Medicine Wheel provides a framework for understanding the universe, the interconnectedness of all things, and the relationship between humans and the natural world.
- Healing and Balance: It is used as a tool for healing, both physical and spiritual. By understanding the balance of the four directions and their corresponding elements, individuals can strive to restore harmony within themselves and with the world around them.
- Spiritual Guidance: The Medicine Wheel offers guidance on how to live a balanced and meaningful life. It encourages self-reflection, introspection, and connection to the spiritual realm.
- Cultural Preservation: The Medicine Wheel is a vital part of Navajo cultural heritage, helping to preserve traditional knowledge, values, and practices.
- Ceremonies and Rituals: The Medicine Wheel is incorporated into various ceremonies and rituals, such as the Enemyway Ceremony, the Blessingway Ceremony, and the Navajo Way of Life.
The Medicine Wheel in Practice
The Navajo Medicine Wheel is not a static concept; it is a dynamic and living tradition that is applied in various ways:
- Personal Reflection: Individuals can use the Medicine Wheel as a tool for personal reflection and self-discovery. By exploring the four directions and their associated meanings, they can gain insights into their strengths, weaknesses, and areas for growth.
- Healing Practices: The Medicine Wheel is used in Navajo healing practices to diagnose and treat illnesses. Navajo healers, known as medicine men or women, utilize the Medicine Wheel to identify imbalances within a person and to restore harmony.
- Ceremonial Use: The Medicine Wheel is central to many Navajo ceremonies, such as the Blessingway ceremony. In these ceremonies, the Medicine Wheel is used to invoke blessings, promote healing, and connect with the spiritual realm.
- Artistic Representation: The Medicine Wheel is often represented in Navajo art forms, such as sand paintings, weaving, and jewelry. These artistic expressions serve as visual reminders of the Medicine Wheel’s symbolism and teachings.
Challenges and Preservation
Like many Indigenous traditions, the Navajo Medicine Wheel has faced challenges due to colonization, cultural assimilation, and modernization. However, the Navajo people have remained resilient in their efforts to preserve and revitalize their cultural heritage.
- Cultural Education: Efforts are being made to educate younger generations about the Medicine Wheel and its significance.
- Language Revitalization: Preserving the Navajo language is crucial for the continued transmission of traditional knowledge.
- Community Support: Navajo communities work together to support traditional healers, medicine people, and cultural practitioners.
- Intertribal Collaboration: Collaboration with other Indigenous communities can help in protecting the sacred knowledge and beliefs associated with medicine wheels.
Conclusion
The Navajo Medicine Wheel is a powerful symbol of the Navajo worldview, representing a holistic understanding of the universe, the interconnectedness of all things, and the path to balance and well-being. It is a living tradition that continues to guide the Navajo people in their spiritual, emotional, and physical journeys. Through understanding the symbolism of the four directions, the elements, and the seasons, individuals can gain insights into themselves and the world around them. The Navajo Medicine Wheel is a testament to the enduring wisdom and resilience of the Navajo people, offering valuable lessons for all who seek a deeper understanding of life.
The Navajo Medicine Wheel serves as a reminder that all things are interconnected and that balance and harmony are essential for a fulfilling life. It encourages us to live in harmony with nature, to cultivate our inner selves, and to walk in a way that honors our ancestors and future generations.