What Does The Medicine Wheel Do?
The Medicine Wheel, also known as the Sacred Hoop, is a sacred symbol and tool of indigenous cultures, primarily in North America. It is a complex and multi-layered construct with deep spiritual and practical significance. While the specific traditions and interpretations vary among different tribes and individuals, the Medicine Wheel serves as a guide to understanding the interconnectedness of all things, promoting balance, healing, and spiritual growth.
Origins and History
The origins of the Medicine Wheel are shrouded in the mists of time, with evidence suggesting its existence for thousands of years. Archaeological findings across North America, such as the Bighorn Medicine Wheel in Wyoming, point to the use of these structures by various indigenous groups.
The Medicine Wheel is not a static concept; it has evolved over time and continues to be adapted and interpreted by contemporary practitioners. It is essential to acknowledge that the knowledge and practices associated with the Medicine Wheel are deeply rooted in indigenous cultures, and respect for these traditions is paramount.
<img src="http://www.crystalwind.ca/images/stories/native/medicine-wheel2.jpg" alt="
What Does The Medicine Wheel Do?
” title=”
What Does The Medicine Wheel Do?
“>
The Basic Structure
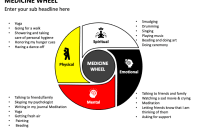
At its core, the Medicine Wheel is a circular arrangement of stones, often with four cardinal directions – East, South, West, and North – marked by specific stones or other features. Within the circle, there may be additional features like spokes, smaller circles, or specific markings. The specific design and materials used vary depending on the tribe and the purpose of the wheel.
The circular shape of the wheel represents the cyclical nature of life, the interconnectedness of all things, and the continuous journey of the individual. The center of the wheel is often seen as the place of the Great Spirit or the source of all creation.
The Four Directions and Their Meanings
The four cardinal directions are fundamental to the Medicine Wheel and represent different aspects of life, the human experience, and the natural world. Each direction is associated with specific colors, elements, seasons, stages of life, and spiritual qualities. While interpretations may vary, here are some common associations:
-
East: The East is typically associated with the color yellow or gold. It symbolizes the rising sun, new beginnings, illumination, inspiration, and the element of air or wind. The East is also connected to the stage of childhood or infancy, representing innocence, potential, and the dawn of understanding. It is a place of hope, clarity, and the seeking of knowledge. The animal associated with the East is often the eagle or hawk, symbolizing vision, perspective, and connection to the divine.
-
South: The South is commonly associated with the color red. It represents the fire element, the warmth of the sun, and the emotions of passion, love, and courage. The South is linked to the stage of youth, symbolizing growth, energy, and the exploration of the world. It is a place of action, creativity, and the development of relationships. The animal associated with the South is often the coyote or the serpent, representing wisdom, playfulness, and the ability to adapt.
-
West: The West is typically associated with the color black or the color of night. It represents the element of water, the setting sun, and the emotions of introspection, healing, and transformation. The West is linked to the stage of adulthood, symbolizing challenges, responsibilities, and the development of wisdom. It is a place of facing fears, letting go of attachments, and embracing change. The animal associated with the West is often the bear, symbolizing introspection, strength, and the power of the subconscious.
-
North: The North is commonly associated with the color white. It represents the element of earth, the stillness of winter, and the emotions of gratitude, wisdom, and the spirit of ancestors. The North is linked to the stage of elderhood, symbolizing experience, reflection, and the passing on of knowledge. It is a place of peace, connection to the past, and the acceptance of death. The animal associated with the North is often the buffalo or the owl, representing wisdom, stability, and the ability to see through illusions.
The Interconnectedness of the Directions
The Medicine Wheel emphasizes the interconnectedness of all directions. Each direction is not separate but rather complements and influences the others. For instance, the East’s new beginnings lead to the South’s growth, which then brings about the West’s transformation and ultimately results in the North’s wisdom. This cyclical process illustrates the continuous flow of life, death, and rebirth.
The Four Aspects of the Self
In addition to the directions, the Medicine Wheel is also used to understand the four aspects of the self:
- Mental: Represents the mind, thoughts, intellect, and knowledge.
- Emotional: Represents feelings, intuition, and relationships.
- Physical: Represents the body, health, and the connection to the earth.
- Spiritual: Represents the connection to the Great Spirit, the soul, and the search for meaning.
By understanding and balancing these four aspects, individuals can strive for wholeness, health, and spiritual growth.
Using the Medicine Wheel
The Medicine Wheel can be used in various ways:
- Meditation and Reflection: Sitting within a Medicine Wheel or visualizing its structure can facilitate meditation, self-reflection, and connection to the natural world.
- Personal Growth: The Medicine Wheel can be used as a framework for personal development. By understanding the qualities and lessons associated with each direction, individuals can identify areas for growth, overcome challenges, and find balance in their lives.
- Healing: The Medicine Wheel can be used as a tool for healing. By exploring the emotions, experiences, and lessons associated with each direction, individuals can release emotional blockages, find peace, and cultivate inner strength.
- Ceremonies and Rituals: The Medicine Wheel is often used in ceremonies and rituals to connect with the spirit world, honor ancestors, and celebrate life’s transitions.
- Understanding Relationships: The Medicine Wheel can be used to understand and improve relationships. By examining the qualities and lessons associated with each direction, individuals can improve their communication, empathy, and understanding of others.
Respect and Cultural Sensitivity
It is essential to approach the Medicine Wheel with respect and cultural sensitivity. The knowledge and practices associated with the Medicine Wheel are sacred to indigenous cultures. If you are not of indigenous descent, it is important to:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the origins, history, and cultural significance of the Medicine Wheel.
- Seek Guidance: If you want to learn more about the Medicine Wheel, seek guidance from a knowledgeable and respected teacher or elder.
- Avoid Appropriation: Avoid taking elements of the Medicine Wheel out of context or using them in a way that disrespects indigenous traditions.
- Acknowledge Indigenous Peoples: Recognize and acknowledge the contributions of indigenous peoples to the knowledge and practices associated with the Medicine Wheel.
Conclusion
The Medicine Wheel is a powerful and profound tool for understanding the interconnectedness of all things, promoting balance, healing, and spiritual growth. It is a symbol of life’s cyclical nature, the importance of harmony, and the continuous journey of the individual. While the specific interpretations and practices may vary, the Medicine Wheel serves as a reminder of the wisdom of indigenous cultures and the importance of living in harmony with ourselves, each other, and the natural world. By approaching the Medicine Wheel with respect, cultural sensitivity, and a willingness to learn, individuals can gain valuable insights and deepen their understanding of life’s mysteries.