Is The Medicine Wheel Bullshit?
The Medicine Wheel, also known as the Sacred Hoop, is an ancient symbol and spiritual concept central to many Indigenous cultures of North America. It is a complex framework that encompasses the interconnectedness of all things, including the human experience, the natural world, and the cosmos. At its core, the Medicine Wheel represents a cyclical understanding of life, death, and rebirth, offering guidance for personal growth, healing, and spiritual connection.
However, the popularity of the Medicine Wheel has also led to its appropriation and commercialization, sparking controversy and raising questions about its authenticity and validity. This article delves into the complexities surrounding the Medicine Wheel, examining its historical and cultural context, its potential benefits, and the criticisms leveled against its misappropriation and misinterpretation.
Historical and Cultural Context:
The origins of the Medicine Wheel are shrouded in the mists of time, with evidence suggesting its presence in various forms across different Indigenous communities for thousands of years. While the specific interpretations and practices associated with the Medicine Wheel vary among different tribes, some common themes and elements persist.
<img src="https://businesslink.ca/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Untitled-presentation-4.jpg" alt="
Is The Medicine Wheel Bullshit?
” title=”
Is The Medicine Wheel Bullshit?
“>
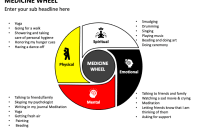
- The Circle: The fundamental shape of the Medicine Wheel is a circle, symbolizing the cyclical nature of life, the interconnectedness of all things, and the wholeness of the universe.
- The Four Directions: The circle is often divided into four quadrants, each representing a cardinal direction (North, South, East, and West), and associated with specific qualities, elements, and teachings.
- The Elements: The four directions are commonly linked to the four elements: earth, air, fire, and water, representing the fundamental building blocks of the physical world.
- The Human Aspects: The Medicine Wheel often incorporates aspects of the human experience, such as physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual aspects. It offers a framework for understanding the interconnectedness of these aspects and their role in personal well-being.
Potential Benefits of the Medicine Wheel:
Proponents of the Medicine Wheel often emphasize its potential benefits for personal growth, healing, and spiritual connection. Some of the key benefits attributed to the practice include:
- Self-Awareness: The Medicine Wheel can serve as a mirror, reflecting the individual’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for growth. It encourages self-reflection and introspection, helping individuals to better understand themselves and their place in the world.
- Personal Growth: By providing a framework for understanding the cyclical nature of life and the interconnectedness of all things, the Medicine Wheel can support personal growth and development. It can guide individuals in overcoming challenges, embracing change, and living a more balanced and fulfilling life.
- Healing: The Medicine Wheel can be used as a tool for healing, both physically and emotionally. It offers a framework for addressing imbalances, processing trauma, and connecting with one’s inner resources for healing.
- Spiritual Connection: The Medicine Wheel can facilitate a deeper connection to the spiritual realm, fostering a sense of awe, wonder, and reverence for the natural world and the cosmos. It can help individuals to connect with their ancestors, their spirit guides, and the Divine.
- Community Building: The Medicine Wheel can be used as a tool for building community, fostering a sense of belonging, and promoting understanding and respect among diverse groups of people.
Criticisms and Concerns:
Despite its potential benefits, the Medicine Wheel has also faced significant criticism, particularly in the context of cultural appropriation and commercialization. Some of the key criticisms include:
- Cultural Appropriation: The widespread adoption of the Medicine Wheel by non-Indigenous individuals and groups, often without proper understanding or respect for its cultural significance, is a form of cultural appropriation. This can result in the trivialization and misrepresentation of Indigenous traditions and beliefs.
- Misinterpretation: The complex and nuanced teachings of the Medicine Wheel are often simplified and misinterpreted by those who are not properly trained or initiated. This can lead to the distortion of its meaning and the perpetuation of inaccurate or harmful practices.
- Commercialization: The commercialization of the Medicine Wheel, through workshops, retreats, and the sale of related products, can undermine its spiritual value and exploit Indigenous knowledge for profit.
- Lack of Authenticity: Some practitioners and teachers of the Medicine Wheel lack the necessary qualifications or cultural authority to teach and practice this sacred tradition. This can lead to the spread of misinformation and the dilution of its spiritual integrity.
- Oversimplification: The Medicine Wheel is often presented as a simple, one-size-fits-all solution to life’s problems, which can be a gross oversimplification of its complexities and nuances.
- Lack of Empirical Evidence: Some critics argue that the claims made about the Medicine Wheel’s effectiveness lack empirical evidence and are based on anecdotal experiences.
Is it Bullshit?
Whether the Medicine Wheel is "bullshit" is a complex question with no easy answer. Its value depends on several factors, including the individual’s intentions, their understanding of the cultural context, and their respect for Indigenous traditions.
- If practiced with respect and understanding: The Medicine Wheel can be a powerful tool for personal growth, healing, and spiritual connection. When practiced with respect for its cultural origins and with guidance from qualified teachers, it can offer profound insights and transformative experiences.
- If appropriated and misused: The Medicine Wheel can become "bullshit" when it is appropriated by those who do not understand or respect its cultural significance. When used without proper understanding, it can be misinterpreted, distorted, and even harmful.
Navigating the Complexities:
For those interested in exploring the Medicine Wheel, it is crucial to approach it with respect, humility, and a willingness to learn. Some guidelines for navigating the complexities of the Medicine Wheel include:
- Education: Research the history and cultural context of the Medicine Wheel, and seek out reputable sources of information.
- Respect: Approach the Medicine Wheel with respect for its cultural origins and the Indigenous communities that hold it sacred.
- Guidance: Seek out qualified teachers and mentors who have a deep understanding of the Medicine Wheel and its cultural context.
- Authenticity: Be wary of commercialized versions of the Medicine Wheel that lack authenticity or are presented without proper cultural context.
- Intention: Approach the Medicine Wheel with clear intentions and a willingness to learn and grow.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Be mindful of the potential for cultural appropriation and avoid practices that exploit or misrepresent Indigenous traditions.
- Skepticism: Maintain a healthy degree of skepticism and critical thinking, and be wary of claims that lack empirical evidence.
- Connection: If possible, seek guidance and teachings from Indigenous Elders or community members.
Conclusion:
The Medicine Wheel is a complex and multifaceted symbol and concept with a rich history and cultural significance. While it offers the potential for personal growth, healing, and spiritual connection, it is also subject to criticism and controversy, particularly in the context of cultural appropriation and commercialization. Whether the Medicine Wheel is "bullshit" depends on the individual’s approach and their commitment to understanding and respecting its cultural origins. By approaching the Medicine Wheel with respect, humility, and a willingness to learn, it can be a valuable tool for personal growth and spiritual development. However, it is essential to be mindful of the potential for cultural appropriation and to avoid practices that exploit or misrepresent Indigenous traditions.