Don Warne’s Medicine Wheel: A Synthesis of Indigenous Wisdom and Modern Healthcare
Don Warne, a member of the Turtle Mountain Band of Chippewa Indians, is a leading figure in the realm of Indigenous health and wellness. He has dedicated his career to bridging the gap between traditional Native American healing practices and the modern healthcare system. His work centers on the Medicine Wheel, a sacred symbol for many Indigenous cultures, representing the interconnectedness of all things and the holistic approach to well-being. This article will explore the key aspects of Don Warne’s Medicine Wheel philosophy and its profound impact on healthcare practices.
Understanding the Medicine Wheel
The Medicine Wheel, also known as the Sacred Hoop, is a fundamental concept in many Indigenous cultures across North America. It is a circular symbol, often depicted with four quadrants, each representing a different aspect of life, such as:
-
<img src="https://i.pinimg.com/236x/c7/2f/22/c72f2202ff4563721ea1834e7e208c1c.jpg" alt="
- The Four Directions: East, South, West, and North. These directions are associated with different qualities, such as new beginnings (East), growth and warmth (South), introspection and completion (West), and wisdom and endurance (North).
- The Four Seasons: Spring, Summer, Autumn, and Winter, reflecting the cyclical nature of life and the changing seasons.
- The Four Stages of Life: Infancy, Youth, Adulthood, and Elderhood, representing the journey of human life from birth to death.
- The Four Elements: Earth, Fire, Water, and Air, embodying the essential components of the natural world and the human body.
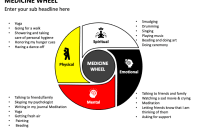
- The Four Aspects of Being: The physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual, recognizing the interconnectedness of these dimensions in achieving overall well-being.
Don Warne’s Medicine Wheel: A Synthesis of Indigenous Wisdom and Modern Healthcare
” title=”
Don Warne’s Medicine Wheel: A Synthesis of Indigenous Wisdom and Modern Healthcare
“>
The Medicine Wheel is not just a static symbol; it is a dynamic system of understanding the world and our place within it. It emphasizes balance and harmony among all the elements and aspects of life. This holistic perspective is a cornerstone of Indigenous healing practices, which focus on treating the whole person, not just the disease or symptoms.
Don Warne’s Vision: Integrating Indigenous Wisdom into Healthcare
Don Warne’s work is rooted in his deep understanding of the Medicine Wheel and his commitment to improving the health and well-being of Indigenous communities. He recognizes the limitations of the modern healthcare system in addressing the complex needs of Native Americans, who often face disparities in healthcare access, cultural sensitivity, and trust in the medical establishment.
Warne’s approach is to integrate the principles of the Medicine Wheel into healthcare practices. He believes that by incorporating Indigenous knowledge and values, healthcare can become more culturally relevant, patient-centered, and effective. His efforts have focused on several key areas:
-
Cultural Competency Training: Warne advocates for training healthcare professionals to understand and respect the cultural beliefs, values, and practices of Indigenous peoples. This includes learning about the Medicine Wheel, traditional healing methods, and the historical and social factors that impact Indigenous health.
-
Creating Culturally Sensitive Healthcare Settings: He promotes the creation of healthcare environments that are welcoming and inclusive of Indigenous patients. This includes incorporating Indigenous art, language, and symbols, as well as providing opportunities for patients to connect with their cultural heritage.
-
Promoting Traditional Healing Practices: Warne recognizes the value of traditional healing methods, such as herbal medicine, sweat lodges, and ceremonies. He works to integrate these practices into the healthcare system, when appropriate and with the consent of the patient, to complement conventional medical treatments.
-
Addressing Social Determinants of Health: Warne understands that health is not solely determined by medical factors; social, economic, and environmental factors also play a significant role. He advocates for addressing the social determinants of health that disproportionately affect Indigenous communities, such as poverty, lack of access to education and employment, and environmental injustice.
-
Community Engagement and Empowerment: Warne emphasizes the importance of involving Indigenous communities in the design and delivery of healthcare services. He believes that community members are the experts on their own health needs and that their voices should be central to the decision-making process. He promotes initiatives that empower Indigenous communities to take control of their own health and well-being.
The Pillars of the Medicine Wheel in Healthcare
Don Warne’s approach to healthcare can be understood through the lens of the four aspects of being, represented in the Medicine Wheel:
-
The Physical: This aspect encompasses the body’s physical health. In Warne’s model, this includes the importance of healthy lifestyles, access to nutritious foods, and addressing chronic diseases. He advocates for preventive care and early intervention to improve physical well-being.
-
The Mental: This aspect focuses on mental health and cognitive function. Warne emphasizes the importance of addressing mental health challenges, such as depression, anxiety, and trauma, that disproportionately affect Indigenous communities. He promotes culturally relevant mental health services, including counseling and therapy.
-
The Emotional: This aspect involves understanding and managing emotions. Warne recognizes the role of emotional well-being in overall health. He advocates for providing support and resources to help individuals process their emotions and build resilience.
-
The Spiritual: This aspect encompasses the connection to something greater than oneself. Warne emphasizes the importance of spirituality in healing and well-being. He supports the integration of traditional spiritual practices into healthcare, when desired by the patient, to promote a sense of connection and purpose.
Impact and Legacy
Don Warne’s work has had a significant impact on the field of Indigenous health. He has helped to raise awareness of the importance of cultural competency, the value of traditional healing practices, and the need to address the social determinants of health. His efforts have inspired healthcare professionals, policymakers, and community members to work together to improve the health and well-being of Indigenous peoples.
Warne’s legacy is one of bridging the gap between Indigenous wisdom and modern healthcare. He has demonstrated that by honoring the values of the Medicine Wheel and incorporating Indigenous perspectives, healthcare can become more effective, equitable, and culturally relevant. His work continues to inspire positive change and create a more holistic and compassionate approach to health and wellness for all.
Challenges and Future Directions
While significant progress has been made, challenges remain in the effort to integrate the Medicine Wheel philosophy into healthcare. These include:
- Resistance to Change: Some healthcare professionals may be resistant to embracing new approaches, particularly those that challenge conventional medical practices.
- Funding and Resources: Adequate funding and resources are needed to support cultural competency training, the integration of traditional healing practices, and the implementation of programs that address the social determinants of health.
- Cultural Appropriation: It is important to ensure that the integration of Indigenous knowledge is done respectfully and ethically, avoiding cultural appropriation and tokenism.
Looking ahead, the future of Don Warne’s Medicine Wheel philosophy lies in:
- Continued Education and Training: Healthcare professionals need ongoing training in cultural competency and Indigenous health.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Building strong partnerships between healthcare providers, Indigenous communities, and policymakers is essential.
- Research and Evaluation: More research is needed to evaluate the effectiveness of integrating the Medicine Wheel philosophy into healthcare.
- Community Empowerment: Supporting Indigenous communities in taking control of their own health and well-being is crucial.
By addressing these challenges and pursuing these directions, Don Warne’s vision of a healthcare system that embraces Indigenous wisdom and values can continue to flourish, creating a healthier and more equitable future for all.